
XBO 1600
Interest in the invention of xenon lamps was first created by Philips Schulz in 1944. Due to wartime restrictions on access to this noble gas, significant progress was not made until John Aldington of the British company Siemens published his research in 1949.
This caused many efforts in the German company Osram to further develop this technology as an alternative to carbon arcs in cinema screening. The xenon lamp has two electrodes that are placed in a glass bubble filled with xenon gas. A high voltage is applied to the electrodes, which momentarily release sparks and light is produced. Xenon lamps were developed in the 1940s and finally introduced in 1951 by the German company Osram.
They were a viable replacement for inefficient carbon lamps and are used in cinemas around the world today. Compared to halogens and LEDs, xenon bulbs not only provide more brightness, improved visibility, and a longer estimated life, approximately 2,000 hours—compared to the average halogen light, which only lasts about 450 to 1,000 hours. It is interesting to know that the 1991 BMW 7 Series was the first car to use xenon to illuminate its path.

Product model:
XBO 1600W Xenon cinema projector lamp (short arc)
Country of manufacture: Germany
Price: $1284
Application:
– 35 mm classic film playback
– Film and digital video projection
– Architecture and light effects
– Simulation of sunlight
Nominal current | 65 A |
Current control range | 50…70 A |
Nominal wattage | 1600 W |
Nominal voltage | 23.0 V |
ORIGIN | GERMANY |
Advantages of the product family:
– Short arc with very high brightness for more brightness of the screen
– Constant color temperature of 6000 Kelvin throughout the life of the lamp
– Simple maintenance
– High arc stability
– Creating momentary light on the screen due to the Hot Restart function
– Wide low light range
Features of the product family:
– Color temperature: approximately 6000 K (daylight)
– Power: 450 to 10000 watts
– Color rendering index: Ra >
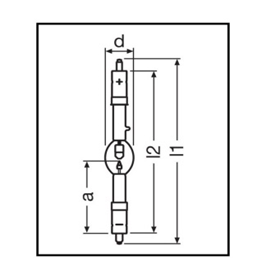
Dimension:
Diameter | 46.0 mm |
Length | 235.0 mm |
Length with base excl. base pins/connection | 205.00 mm |
Light center length (LCL) | 95.0 mm |
Cable/wire length, input side | – |
Electrode gap cold | 3.8 mm |
Product weight | 301.00 g |
Temperatures & operating conditions
Max. Permitted ambient temp. pinch point | 230 °C |
Lifespan
Lifespan | 2500 H |
Additional product data
Base anode (standard designation) | SFa27-11 |
Base cathode (standard designation) | SFcX27-8 |
Product Datasheet
Cooling | Forced |
Burning position | s20/p20 |