A Comparison of Smart Lighting Systems: ZigBee, KNX, or Wi-Fi?
The automation of buildings and homes has seen significant growth in recent years. Among the various systems used for controlling lighting and other equipment, three prominent and widely-used technologies—KNX, ZigBee, and Wi-Fi—have garnered considerable attention. Choosing among these options for different projects depends on factors such as project scale, type of equipment, budget, security, and customization needs.
In this article, we will examine each of these systems in terms of their nature, advantages, capabilities, main components, and applications, and ultimately provide a detailed comparison among them.
What is the KNX System?
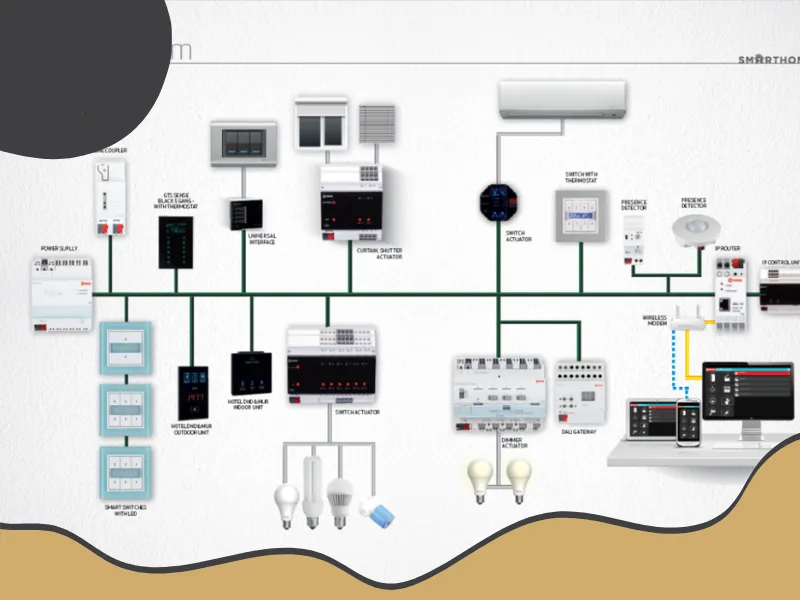
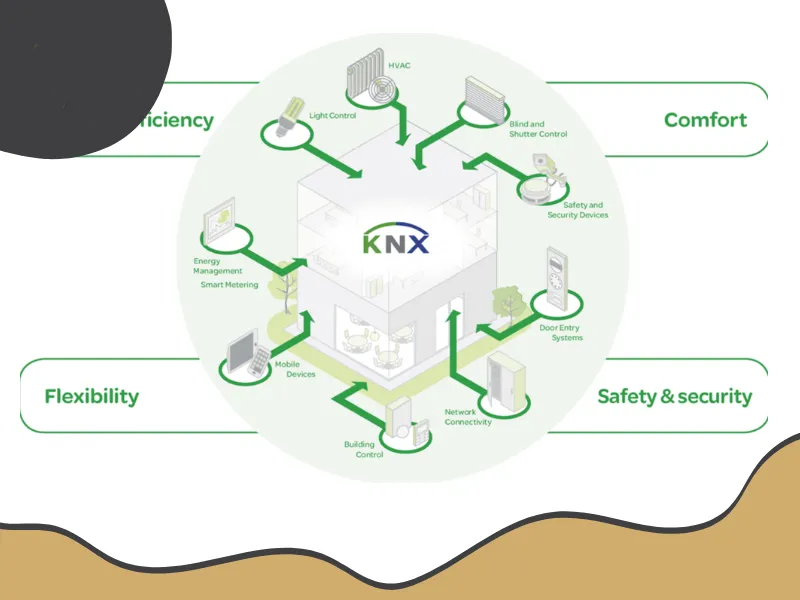
KNX is an open protocol and global standard for building automation that has been recognized as an international standard (ISO/IEC 14543) since 1999. This system is used to control all components of a smart building, such as lighting, heating and cooling, blinds, security systems, and audio-visual equipment.
Advantages of KNX
-
Global Stability and Standardization: KNX is a stable international standard that is usable and expandable worldwide.
-
Integration with Various Brands: Products from different brands can be easily integrated with KNX.
-
Energy Consumption Reduction: Precise control of equipment leads to reduced energy costs.
-
Central or Remote Control: Users can have full control over systems from inside or outside the building.
Capabilities of KNX
-
Control of lighting, ventilation, audio systems, electric blinds, and more.
-
Setting up automated scenarios based on time, presence of individuals, or natural light.
-
Integration with security systems.
-
Control via mobile devices, tablets, or central panels.
Main Components of KNX
-
Sensors: Detect motion, light, temperature, etc.
-
Actuators: Execute commands such as turning lights on/off.
-
Control Panels: User interfaces for managing the system.
-
Power Supply Units: Provide necessary power to the system.
-
Communication Media: Wiring or wireless methods for data transmission.

What is ZigBee?
ZigBee is a wireless communication protocol designed for low-power digital radio connections. It is commonly used in home automation, industrial control, and medical data collection.
Advantages of ZigBee
-
Low Power Consumption: Ideal for battery-operated devices.
-
Mesh Networking: Devices can relay data for others, enhancing network reliability.
-
Scalability: Suitable for both small and large-scale installations.
-
Interoperability: Supports integration with various devices and brands.
Capabilities of ZigBee
-
Control of lighting, thermostats, security systems, and more.
-
Real-time monitoring and control via mobile apps.
-
Automation based on sensors and predefined scenarios.
-
Remote access and control over the internet.
-
-
Main Components of ZigBee
-
Coordinator: Manages the network and stores information.
-
Routers: Extend network range and relay data.
-
End Devices: Perform specific functions like sensing or actuating.
-
Gateways: Connect ZigBee networks to the internet or other networks.
What is the Wi-Fi System?
Wi-Fi is a wireless networking technology that allows devices to connect to the internet or communicate with one another wirelessly within a particular area. It is widely used in homes and businesses for various applications, including smart lighting.
Advantages of Wi-Fi
-
High Data Transfer Rates: Suitable for bandwidth-intensive applications.
-
Wide Device Compatibility: Most modern devices support Wi-Fi.
-
No Need for Additional Hubs: Devices can connect directly to existing Wi-Fi networks.
-
Ease of Installation: Simple setup processes for most devices.
Capabilities of Wi-Fi
-
Remote control of lighting and other devices via internet-connected apps.
-
Integration with voice assistants like Alexa or Google Assistant.
-
Scheduling and automation features.
-
Real-time notifications and monitoring.
Main Components of Wi-Fi Systems
-
Wi-Fi Routers: Provide wireless internet connectivity.
-
Smart Devices: Include bulbs, switches, and sensors with Wi-Fi capabilities.
-
Control Apps: Mobile or web applications for managing devices.
Final Comparison: KNX, ZigBee, or Wi-Fi?
| Feature | KNX | ZigBee | Wi-Fi |
|---|---|---|---|
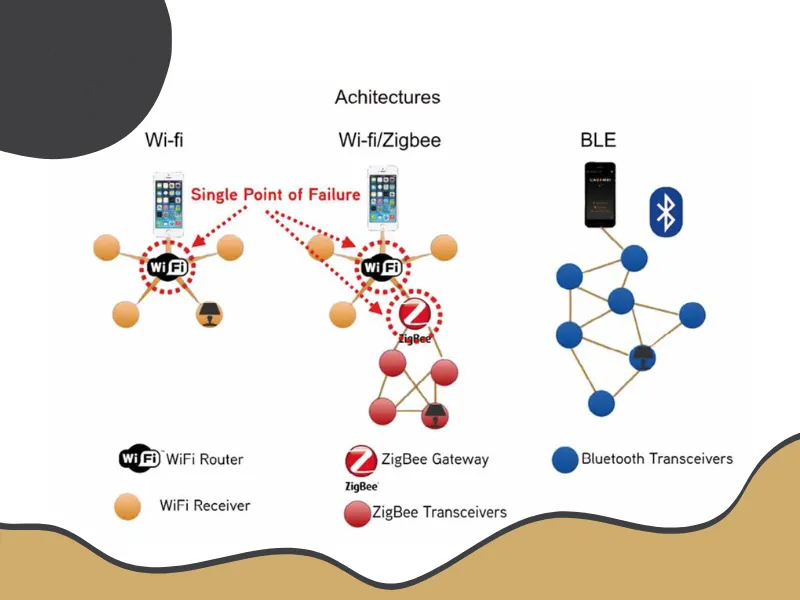
| Communication | Wired (with wireless options) | Wireless (Mesh Network) | Wireless (Wi-Fi Network) |
| Power Consumption | Low | Very Low | High |
| Scalability | High | High | Moderate |
| Installation Complexity | High (Professional setup) | Moderate | Low (DIY-friendly) |
| Interoperability | High (Standardized) | High (Multiple vendors) | Varies (Depends on device) |
| Cost | High | Moderate | Low |
| Reliability | Very High | High | Moderate |
| Control Options | Centralized and Remote | Remote via Apps | Remote via Apps |
Suitable Projects for Each System
-
KNX: Ideal for large-scale projects like commercial buildings, hotels, and luxury residences where reliability and integration are paramount.
-
ZigBee: Suitable for medium to large homes and offices that require a balance between scalability and ease of installation.
-
Wi-Fi: Best for small to medium-sized homes where cost and simplicity are primary concerns.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can these systems be integrated together?
A: Yes, through the use of gateways and integration platforms, it’s possible to combine different systems for enhanced functionality.
Which system offers the best security?
A: KNX and ZigBee have robust security features, but Wi-Fi systems depend heavily on the security of the home network.
Is professional installation required for all systems?
A: KNX typically requires professional installation, while ZigBee and Wi-Fi systems can often be set up by the user.