Comprehensive Review of Network Cable Types
Network cables serve as one of the most critical components in communication systems and computer networks, playing a key role in data transfer between various devices. With the evolution of technologies and the growing need for swift and reliable data transmission, a diverse range of network cables has been introduced to the market. This article delves into a detailed examination of different network cable types, their characteristics, advantages and disadvantages of each type and their applications.
1. Twisted Pair Cables
Twisted pair cables are one of the most common and oldest types of network cables used for data transmission in local area networks (LANs). These cables consist of several pairs of copper wires twisted together to reduce noise and electromagnetic interference.
UTP (Unshielded Twisted Pair) Cables
UTP cables are the most common type of network cables that do not have any additional shielding to prevent electromagnetic interference. These cables are very popular in home and small office networks due to their low cost and easy installation.
UTP Cable features:
• Affordable price :The price of UTP cables is more affordable compared to other types of cables, and for this reason, they are very popular in small projects.
• Easy installation :The small diameter of these cables, their flexibility, make installation in various environments easy.
• Distance limit :They usually have a good performance up to distances of about 100 meters, and in longer distances, they need a booster.
UTP Cable applications:
• Local Area Networks (LANs)
• Home networks
• Telephone systems
STP (Shielded Twisted Pair) Cables
STP cables, like UTP cables, have twisted pairs of wires, but their difference is the presence of a shielding layer for each pair of wires, which prevents the effects of external noise and electromagnetic interference. These cables are used in industrial environments and places where there is a lot of electronic equipment.
STP Cable Features:
• Better Noise Protection: The shields in STP cable prevent the entry of external noise and interference.
• Application in Noisy Environments: For environments with high electromagnetic noise (such as factories and industrial centers), this cable is a suitable choice.
STP Cable Applications:
• Industrial environments and factories
• Noise-sensitive networks
• Large infrastructures
FTP (Foiled Twisted Pair) Cables
Another type of twisted pair cables is FTP cables, in which a layer of metal foil is wrapped around all the pairs to protect against electromagnetic interference. These cables can also be used in environments with high electromagnetic interference.
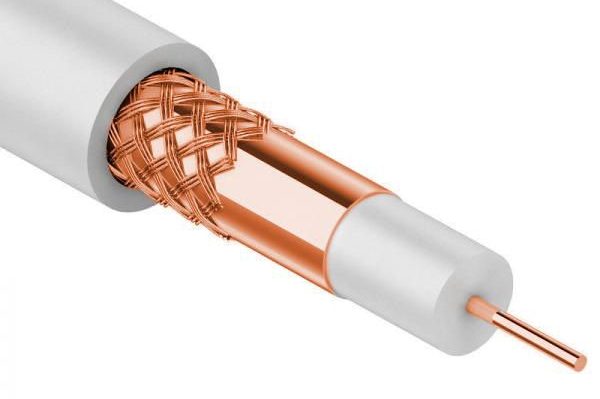
2. Coaxial Cables
Coaxial cables were popular for computer networks in past decades and are still used in television and radio communication systems. These cables consist of a central conductor covered with an insulating layer and a metal layer that acts as a shield.
• Radio communications
• Older computer networks
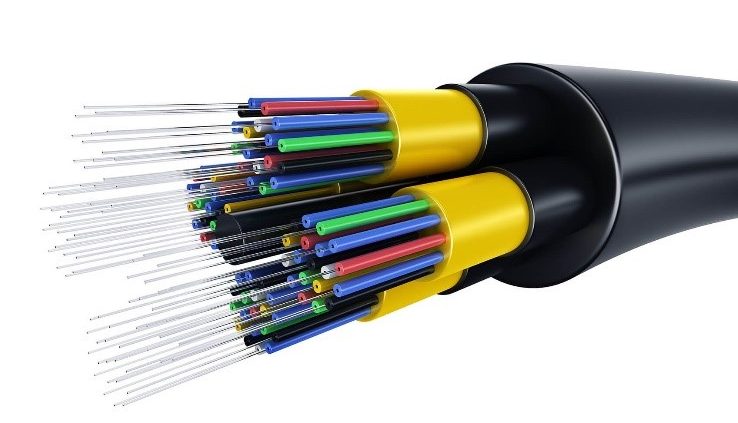
3. Fiber Optic Cables
Fiber optic cables are the newest and most advanced type of network cables that use thin strands of glass or plastic instead of copper wires.
Information is transmitted in these cables in the form of light pulses, which significantly increases the speed and quality of data transmission.
Fiber Optic Cable Features:
• Very High Speed: These cables can transmit data at a much higher speed than copper cables.
• Noise Immunity: Fiber optic cables are not affected by electromagnetic noise at all.
• Long Transmission Distance: These cables are capable of transmitting data over very long distances (up to hundreds of kilometers) without the need for amplifiers.
Types of Fiber Optic Cables:
• Single-Mode Fiber Optic: This type of cable is used for data transmission over very long distances (even up to several hundred kilometers).
• Multi-Mode Fiber Optic: This type of cable is used for shorter distances and more common applications such as local networks.
Fiber Optic Cable Applications:
• High-speed internet infrastructures
• Intercity and international communication networks
• Data centers
• Telecommunication systems

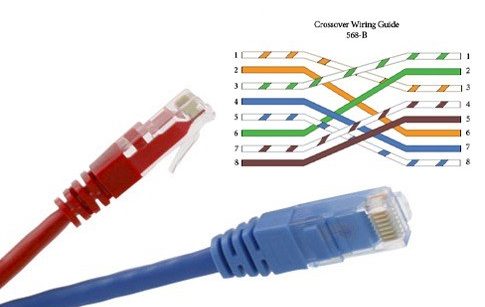
4. Crossover Cables
Crossover cables are a special type of twisted-pair cables that are used to directly connect two similar devices. In this type of cable, some of the wires inside the cable are connected in a cross pattern so that the two devices can communicate with each other without the need for a switch or hub.
Crossover Cable Applications:
• Direct connection of two computers
• Connection of two routers or switches
• Direct connection between two similar devices
5. Network Cables Cat5, Cat6, and Cat7
Network cables are usually classified based on specific standards, which include Cat5, Cat6, and Cat7. Each of these cables is designed for a specific speed and bandwidth.
a) Cat5 Cables
Transfer speed: Up to 100 Mbps
Bandwidth: Up to 100 MHz
Applications: Small home and office networks
b) Cat6 Cables
Transfer speed: Up to 10 Gbps over short distances
Bandwidth: Up to 250 MHz
Applications: Larger and professional networks
c) Cat7 Cables
Transfer speed: Up to 10 Gbps
Bandwidth: Up to 600 MHz
Applications: Infrastructure of very large networks and data centers
Conclusion
Due to the wide variety of network cables, choosing the right cable depends on the network needs, usage environment, and project budget. For small home and office networks, twisted-pair cables (UTP and STP) are very suitable options. In contrast, for larger and high-speed projects, fiber optic cables are considered the best option.

Leave a Reply