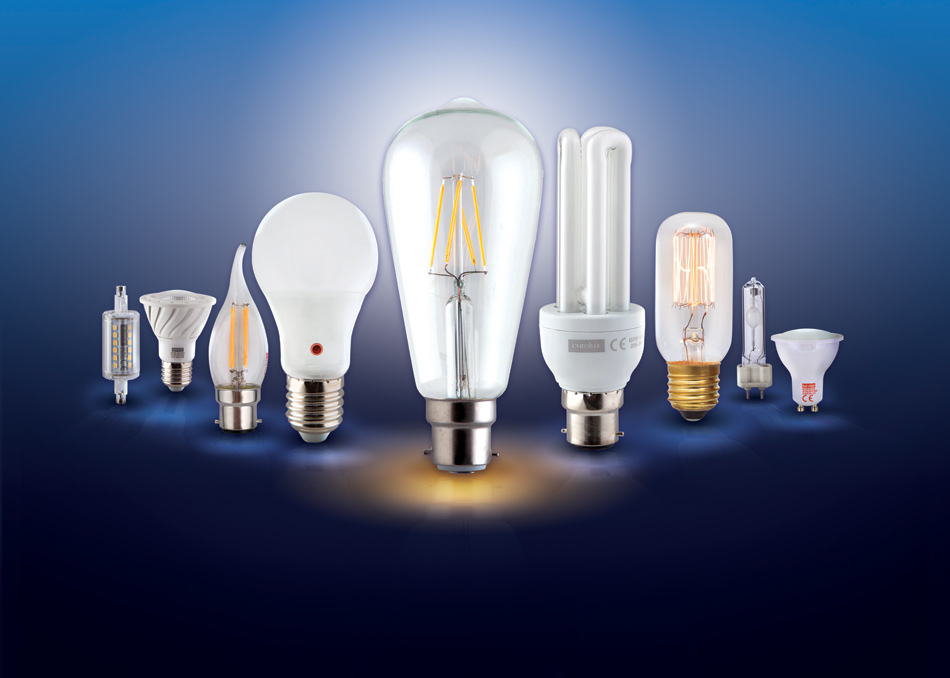
Comparison of conventional lamps with each other
In this article from the ZEM Group website, we will discuss the comparisons of conventional lamps. When considering the types of bulbs, it’s important to note that the market is full of a variety of bulbs with different qualities and technologies, including incandescent, metal halide, fluorescent, LED, and SMD. In this article, we are going to review different types of lamps and finally introduce you to the best type.
Explanation: This text examines and compares different types of lamps, focusing on different technologies and qualities that are available in the market. The goal is to help readers choose the best type of light bulb based on their needs and desired standards.
Types of lamps used in different environments
 Incandescent lamps
Incandescent lamps
The light emitted by incandescent lamps is warm and uniform and closely resembles natural light, which makes it the best artificial light. However, these lamps are not economical in terms of the efficiency of converting electricity into light and convert less than 5% of the received energy into light. For this reason, countries such as Australia have introduced lamps with higher efficiency instead.
In fact, it can be argued that why incandescent lamps, despite producing warm and natural light, are no longer popular due to the lack of efficiency in converting electricity to light. This has led to a shift towards more efficient light bulbs in some countries.

fluorescent lamps
Mercury fluorescent lamps are more expensive than incandescent lamps, but they have a longer life. These lamps consume less than incandescent lamps, however, they have significant disadvantages. The biggest drawback of these lamps is the dangers they pose to human health, especially due to the ultraviolet rays and mercury they contain.
 Mercury lamps
Mercury lamps
Mercury vapor lamps are known for their high light efficiency and long life. The suitable light color of these lamps makes them ideal for lighting outdoor spaces such as parks, sidewalks and factory halls. However, due to the dangers of mercury vapor for the environment, their production has been banned in EU member states. Also, these lamps have a high energy loss, which indicates that the era of their use in providing lighting is gradually coming to an end.

Sodium vapor lamps
Sodium vapor lamps, with their characteristic yellow light production, are ideal for certain applications such as lighting industrial areas or docks. This yellow light is very useful due to its high efficiency in environments with different weather conditions and visibility in fog. However, the color of the light and its unfavorable reflection make them not suitable for use in environments that require more color accuracy, such as shopping centers or parks. This limitation in the use of sodium vapor lamps shows the importance of choosing the right type of lighting for each environment.

LED lamps
LED lamps, with their advanced technology, are becoming an alternative to more traditional types of lamps. These lamps, which are made of light emitting diodes, are designed to improve the quality of light and increase energy efficiency. LEDs are produced in different watt ranges and are used for various applications such as interior lighting of homes, offices, stores and even street and park lighting. By offering a wide range of colors and light intensities, these lamps provide high flexibility in lighting design.
Light emitting diode (LED) is a type of diode that emits energy in the form of light when current passes through it. These lamps use a very small amount of energy to produce light and can produce various colors. Among the advantages of using LED lamps, we can point out the power consumption of only ten percent of conventional lamps, a long life of up to 50,000 hours, and extraordinary exposure. For this reason, their use is becoming more widespread day by day, and many believe that LED lamps will take the market from their competitors in the future. Now, many large lighting equipment manufacturing companies, especially in the field of home lighting, have focused their activities on LED lamps.
LED lamps have become a popular choice among consumers due to their high durability and lower energy consumption than traditional types. In addition, these lamps are more environmentally friendly because they do not contain hazardous substances such as mercury and reduce greenhouse gas emissions. Despite the higher initial price, their energy saving and longer life make them an economical option in the long run. These features have caused LEDs to be quickly replaced by other types of lamps.
On the other hand, considering that LEDs can be fed with alternating current (AC) and direct current (DC) and have little consumption, they can use solar energy sources or batteries for their energy supply. At present, the use of these lighting sources in passages, streets, roads, decorating and beautifying different places, considering the high cost of maintenance and maintenance of traditional lighting sources and long life and saving energy up to 90%, is technically and economically justified. Is. Although LED lamps do not have natural light like incandescent lamps, they do not have harmful UV and IR rays, which are present in fluorescent and energy-saving lamps.

Metal halide lamps
Metal halide lamps, which are similar in structure to mercury vapor lamps, except that some halogen salts have been added to them. These additives help to improve the color quality and increase the light output of these lamps. For this reason, today the use of metal halide lamps is increasingly expanding and they are proposed as an alternative to other types of lamps. These lamps are produced in a wide range of powers, from 20 to 2000 watts, and are used in various places such as interior lighting of houses, factory halls, city roads, sports stadiums and large areas. Metal halide lamps have two bubble layers, with the outer bubble blocking UV radiation. If this bubble breaks, using the lamp can be very dangerous and cause serious damage to human eyes and skin.
Comparison of LED lamps with metal halide:
Longevity: In comparison, metal halide lamps even in the best conditions only last up to 20,000 hours (usually between 16,000 and 20,000 hours). In contrast, LED lamps can last between 50,000 and 60,000 hours, significantly reducing maintenance costs.
1.Response time: LED lamps turn on immediately after receiving voltage (less than 20 microseconds), while metal halide lamps need about 5 minutes to reach their maximum light. Also, metal halide lamps cannot turn on immediately after being off for a while and need time to cool down.
2.Turning on and off: The life of LED lamps does not depend on the number of times they are turned on and off, and they can be turned on and off millions of times. Meanwhile, the life of metal halide lamps decreases every time they are turned on and off.
3.Energy consumption and side costs: Metal halide lamps require high current, especially high wattage models, which may require rewiring, which means more cost and time. On the other hand, LED projectors can use existing wiring due to their lower consumption.
4.Color change: In metal halide lamps, color filters are usually used to change the color. This method is less flexible and almost obsolete. On the other hand, changing the color in LED lamps can be done easily and without the need for mechanical devices.
5.Adjusting the light intensity: It is not possible to adjust the light in metal halide lamps, while it is possible in LED lamps using PWM technology.
6.Adjusting the beam angle: The light of metal halide lamps is difficult to control, while LED lamps have a completely controllable light due to the presence of lenses with arbitrary angles.
7.Starting current: Metal halide lamps need more current at the beginning, while LED lamps do not.
8.Light reduction over time: The light intensity of metal halide lamps decreases over time, while LED lamps have less light reduction.
With these things in mind, the use of LED lamps seems increasingly justified compared to metal halide lamps.






 Incandescent lamps
Incandescent lamps
 Mercury lamps
Mercury lamps